Asia
|
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.6% of the Earth's total surface area (or 29.9% of its land area) and with approximately 4 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population.
Asia is traditionally defined as part of the landmass of Eurasia with the western portion of the latter occupied by Europe located to the east of the Suez Canal, east of the Ural Mountains and south of the Caucasus Mountains (or the Kuma-Manych Depression) and the Caspian and Black Seas.It is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. Given its size and diversity, Asia a toponym dating back to classical antiquity is more a cultural concept incorporating a number of regions and peoples than a homogeneous physical entity.
The wealth of Asia differs very widely among and within its regions, due to its vast size and huge range of different cultures, environments, historical ties and government systems.
Asia is traditionally defined as part of the landmass of Eurasia with the western portion of the latter occupied by Europe located to the east of the Suez Canal, east of the Ural Mountains and south of the Caucasus Mountains (or the Kuma-Manych Depression) and the Caspian and Black Seas.It is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. Given its size and diversity, Asia a toponym dating back to classical antiquity is more a cultural concept incorporating a number of regions and peoples than a homogeneous physical entity.
The wealth of Asia differs very widely among and within its regions, due to its vast size and huge range of different cultures, environments, historical ties and government systems.
Etymology
The term "Asia" is originally a concept exclusively of Western civilization. The peoples of ancient Asia (Chinese, Japanese, Indians, Persians, Arabs etc.) never conceived the idea of Asia, simply because they did not see themselves collectively. In their perspective, they were vastly varied civilizations, contrary to ancient European belief.
The word Asia originated from the Greek word σία, first attributed to Herodotus (About 440 BC) in reference to Anatolia or in describing the Persian Wars to the Persian Empire, in contrast to Greece and Egypt. Herodotus comments that he is puzzled as to why three women's names are used to describe one enormous and substantial land mass (Europa, Asia, and Libya, referring to Africa), stating that most Greeks assumed that Asia was named after the wife of Prometheus (i.e. Hesione), but that the Lydians say it was named after Asias, son of Cotys, who passed the name on to a tribe in Sardis. Even before Herodotus, Homer knew of two figures in the Trojan War named Asios; and elsewhere he describes a marsh as ασιος (Iliad 2, 461).
Usage of the term soon became common in ancient Greece, and subsequently by the ancient Romans.Ancient and medieval European maps depict the Asian continent as a "Huge amorphous blob" extending eastward.It was presumed in antiquity to end with India the Macedonian king Alexander the Great believing he would reach the "End of the world" upon his arrival in the East.
The word Asia originated from the Greek word σία, first attributed to Herodotus (About 440 BC) in reference to Anatolia or in describing the Persian Wars to the Persian Empire, in contrast to Greece and Egypt. Herodotus comments that he is puzzled as to why three women's names are used to describe one enormous and substantial land mass (Europa, Asia, and Libya, referring to Africa), stating that most Greeks assumed that Asia was named after the wife of Prometheus (i.e. Hesione), but that the Lydians say it was named after Asias, son of Cotys, who passed the name on to a tribe in Sardis. Even before Herodotus, Homer knew of two figures in the Trojan War named Asios; and elsewhere he describes a marsh as ασιος (Iliad 2, 461).
Usage of the term soon became common in ancient Greece, and subsequently by the ancient Romans.Ancient and medieval European maps depict the Asian continent as a "Huge amorphous blob" extending eastward.It was presumed in antiquity to end with India the Macedonian king Alexander the Great believing he would reach the "End of the world" upon his arrival in the East.
Geography of Asia
Asia, comprising approximately fifty countries. It has an area, including islands, of roughly 44,579,000 km². Asia is joined to Africa by the Isthmus of Suez and to Europe by a long border generally following the Ural Mountains.
Medieval Europeans considered Asia as a continent, a distinct landmass. The European concept of the three continents in the Old World goes back to classical antiquity with the etymology of the word rooted in the ancient Near and Middle East. The demarcation between Asia and Africa is the isthmus of Suez and the Red Sea.
The boundary between Asia and Europe is commonly believed to run through the Dardanelles, the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus, the Black Sea, the Caucasus Mountains, the Caspian Sea, the Ural River to its source, and the Ural Mountains to the Kara Sea near Kara, Russia.
However, modern discovery of the extent of Africa and Asia made this definition rather anachronistic, especially in the case of Asia, which would have several regions that would be considered distinct landmasses if these criteria were used (For example, South Asia and East Asia).
Geologists and physical geographers no longer consider Europe and Asia to be separate continents. It is either defined in terms of geological landmasses (physical geography) or tectonic plates (geology). In the former case, Europe is a western peninsula of Eurasia or the Africa-Eurasia landmass. In the latter, Europe and Asia are parts of the Eurasian plate, which excludes the Arabian and Indian tectonic plates.
In human geography, there are two schools of thought. One school follows historical convention and treats Europe and Asia as different continents, categorizing Europe, East Asia (the Orient), South Asia and the Middle East (Arabia and Persia) as specific regions for more detailed analysis.
The other schools equate the word "Continent" in terms of geographical region when referring to Europe, and use the term "Region" to describe Asia in terms of physical geography. It is becoming increasingly common to substitute the term "Region" for "continent" because in linguistic terms, "Continent" implies a distinct landmass.
There is much confusion in European languages with the term "Asian", which almost always refers to a subcategory of people from Asia rather than referring to "Asian" defined in term of "Asia", because a category implies homogeneity. In American English, Asian refers to East Asians, while in British English, Asian refers to South Asians. Some definitions of Asia exclude Turkey, the Middle East, or Russia. The term is sometimes used more strictly in reference to Asia Pacific, which does not include the Middle East or Russia, but does include islands in the Pacific Ocean — many of which are considered part of Australasia or Oceania. Asia contains the Indian subcontinent, Arabian peninsula, as well as a piece of the North American plate in Siberia.
Medieval Europeans considered Asia as a continent, a distinct landmass. The European concept of the three continents in the Old World goes back to classical antiquity with the etymology of the word rooted in the ancient Near and Middle East. The demarcation between Asia and Africa is the isthmus of Suez and the Red Sea.
The boundary between Asia and Europe is commonly believed to run through the Dardanelles, the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus, the Black Sea, the Caucasus Mountains, the Caspian Sea, the Ural River to its source, and the Ural Mountains to the Kara Sea near Kara, Russia.
However, modern discovery of the extent of Africa and Asia made this definition rather anachronistic, especially in the case of Asia, which would have several regions that would be considered distinct landmasses if these criteria were used (For example, South Asia and East Asia).
Geologists and physical geographers no longer consider Europe and Asia to be separate continents. It is either defined in terms of geological landmasses (physical geography) or tectonic plates (geology). In the former case, Europe is a western peninsula of Eurasia or the Africa-Eurasia landmass. In the latter, Europe and Asia are parts of the Eurasian plate, which excludes the Arabian and Indian tectonic plates.
In human geography, there are two schools of thought. One school follows historical convention and treats Europe and Asia as different continents, categorizing Europe, East Asia (the Orient), South Asia and the Middle East (Arabia and Persia) as specific regions for more detailed analysis.
The other schools equate the word "Continent" in terms of geographical region when referring to Europe, and use the term "Region" to describe Asia in terms of physical geography. It is becoming increasingly common to substitute the term "Region" for "continent" because in linguistic terms, "Continent" implies a distinct landmass.
There is much confusion in European languages with the term "Asian", which almost always refers to a subcategory of people from Asia rather than referring to "Asian" defined in term of "Asia", because a category implies homogeneity. In American English, Asian refers to East Asians, while in British English, Asian refers to South Asians. Some definitions of Asia exclude Turkey, the Middle East, or Russia. The term is sometimes used more strictly in reference to Asia Pacific, which does not include the Middle East or Russia, but does include islands in the Pacific Ocean — many of which are considered part of Australasia or Oceania. Asia contains the Indian subcontinent, Arabian peninsula, as well as a piece of the North American plate in Siberia.
Climate of Asia
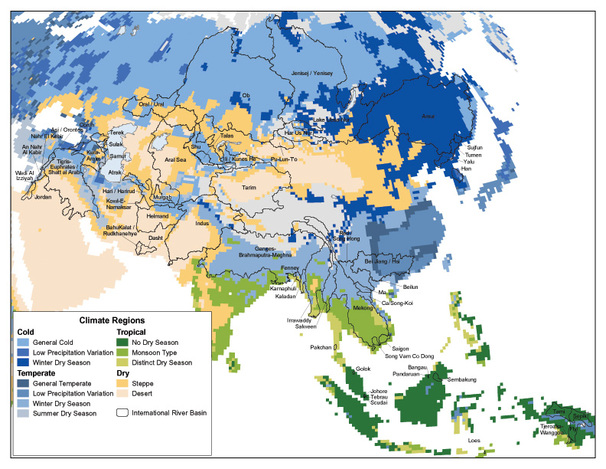
The Climate of Asia is moist across southeast sections, and dry across much of the interior. Some of the largest daily temperature ranges on Earth occur in western sections of Asia. The monsoon circulation dominates across southern and eastern sections, due to the presence of the Himilayas forcing the formation of a thermal low which draws in moisture during the summer.
Southwestern sections of the continent are hot. Siberia is one of the coldest places in the Northern Hemisphere, and can act as a source of arctic air masses for North America. The most active place on Earth for tropical cyclone activity lies northeast of the Philippines and south of Japan, and the phase of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation modulates where in Asia landfall is more likely to occur.
Southwestern sections of the continent are hot, while northeast sections are the coldest.
The highest temperature recorded within the continent was 53.9 °C (129.0 °F) at Tirat Tsvi, Israel on June 21, 1942.West-central Asia experiences some of the largest diurnal temperature ranges on Earth. The lowest temperature measured was −68 °C (−90 °F) at Verkhoyansk and Oymyakon, both in Sakha Republic of Russia on February 7, 1892 and February 6, 1933 respectively.
Southwestern sections of the continent are hot. Siberia is one of the coldest places in the Northern Hemisphere, and can act as a source of arctic air masses for North America. The most active place on Earth for tropical cyclone activity lies northeast of the Philippines and south of Japan, and the phase of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation modulates where in Asia landfall is more likely to occur.
Southwestern sections of the continent are hot, while northeast sections are the coldest.
The highest temperature recorded within the continent was 53.9 °C (129.0 °F) at Tirat Tsvi, Israel on June 21, 1942.West-central Asia experiences some of the largest diurnal temperature ranges on Earth. The lowest temperature measured was −68 °C (−90 °F) at Verkhoyansk and Oymyakon, both in Sakha Republic of Russia on February 7, 1892 and February 6, 1933 respectively.
History of Asia

Ruins of Ur,Tell el-Mukayyar, Iraq
The history of Asia can be seen as the distinct histories of several peripheral coastal regions: East Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia and the Middle East, linked by the interior mass of the Central Asian steppes.
The coastal periphery was home to some of the world's earliest known civilizations, each of them developing around fertile river valleys. The civilizations in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley and the Huanghe shared many similarities. These civilizations may well have exchanged technologies and ideas such as mathematics and the wheel. Other innovations, such as writing, seem to have been developed individually in each area. Cities, states and empires developed in these lowlands.
The central steppe region had long been inhabited by horse-mounted nomads who could reach all areas of Asia from the steppes. The earliest postulated expansion out of the steppe is that of the Indo-Europeans, who spread their languages into the Middle East, South Asia, and the borders of China, where the Tocharians resided. The northernmost part of Asia, including much of Siberia, was largely inaccessible to the steppe nomads, owing to the dense forests, climate and tundra. These areas remained very sparsely populated.
The center and the peripheries were mostly kept separated by mountains and deserts. The Caucasus and Himalaya mountains and the Karakum and Gobi deserts formed barriers that the steppe horsemen could cross only with difficulty. While the urban city dwellers were more advanced technologically and socially, in many cases they could do little in a military aspect to defend against the mounted hordes of the steppe. However, the lowlands did not have enough open grasslands to support a large horsebound force; for this and other reasons, the nomads who conquered states in China, India, and the Middle East often found themselves adapting to the local, more affluent societies.
The Islamic Caliphate took over the Middle East and Central Asia during the Muslim conquests of the 7th century. The Mongol Empire conquered a large part of Asia in the 13th century, an area extending from China to Europe.
The coastal periphery was home to some of the world's earliest known civilizations, each of them developing around fertile river valleys. The civilizations in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley and the Huanghe shared many similarities. These civilizations may well have exchanged technologies and ideas such as mathematics and the wheel. Other innovations, such as writing, seem to have been developed individually in each area. Cities, states and empires developed in these lowlands.
The central steppe region had long been inhabited by horse-mounted nomads who could reach all areas of Asia from the steppes. The earliest postulated expansion out of the steppe is that of the Indo-Europeans, who spread their languages into the Middle East, South Asia, and the borders of China, where the Tocharians resided. The northernmost part of Asia, including much of Siberia, was largely inaccessible to the steppe nomads, owing to the dense forests, climate and tundra. These areas remained very sparsely populated.
The center and the peripheries were mostly kept separated by mountains and deserts. The Caucasus and Himalaya mountains and the Karakum and Gobi deserts formed barriers that the steppe horsemen could cross only with difficulty. While the urban city dwellers were more advanced technologically and socially, in many cases they could do little in a military aspect to defend against the mounted hordes of the steppe. However, the lowlands did not have enough open grasslands to support a large horsebound force; for this and other reasons, the nomads who conquered states in China, India, and the Middle East often found themselves adapting to the local, more affluent societies.
The Islamic Caliphate took over the Middle East and Central Asia during the Muslim conquests of the 7th century. The Mongol Empire conquered a large part of Asia in the 13th century, an area extending from China to Europe.
Countries and territories
There are approximately fifty Countries and territories in Asia and 48 countries.
|
|
Religion in Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, with millions of different peoples following a wide variety of different religions. Asia was the birthplace of most of the world's mainstream religions including Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, Islam, Jainism, Judaism, Sikhism, Taoism, Zoroastranism as well as many other beliefs.
Abrahamic religions

The Kaaba, holiest place in Islam
The Abrahamic religions of Judaism, Christianity and Islam originated in West Asia.
Judaism, the oldest of the Abrahamic faiths, is practiced primarily in Israel (Which has the world's largest Jewish population According to The Jewish Population of the World,2010) though small communities exist in other countries, such as the Bene Israel in India.
In the Philippines and East Timor, Roman Catholicism is the predominant religion; it was introduced by the Spaniards and the Portuguese, respectively. In Armenia, Cyprus, Georgia and Russia, Eastern Orthodoxy is the predominant religion. Various Christian denominations have adherents in portions of the Middle East, as well as China and India.
The world's largest Muslim community (Within the bounds of one nation) is in Indonesia. South Asia (Mainly Pakistan, India and Bangladesh) holds 30% of Muslims. There are also significant Muslim populations in China, Iran, Malaysia, southern Philippines (Mindanao), Russia and most of West Asia and Central Asia.
Judaism, the oldest of the Abrahamic faiths, is practiced primarily in Israel (Which has the world's largest Jewish population According to The Jewish Population of the World,2010) though small communities exist in other countries, such as the Bene Israel in India.
In the Philippines and East Timor, Roman Catholicism is the predominant religion; it was introduced by the Spaniards and the Portuguese, respectively. In Armenia, Cyprus, Georgia and Russia, Eastern Orthodoxy is the predominant religion. Various Christian denominations have adherents in portions of the Middle East, as well as China and India.
The world's largest Muslim community (Within the bounds of one nation) is in Indonesia. South Asia (Mainly Pakistan, India and Bangladesh) holds 30% of Muslims. There are also significant Muslim populations in China, Iran, Malaysia, southern Philippines (Mindanao), Russia and most of West Asia and Central Asia.
Dharmic and Taoist

The Harimandir Sahib, known popularly as the Golden Temple, is a sacred shrine for Sikhs.
The religions of Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism and Sikhism originated in India, South Asia. In East Asia, particularly in China and Japan, Confucianism, Taoism and Zen Buddhism took shape.
Over 80% of the populations of both India and Nepal adhere to Hinduism, alongside significant communities in Bangladesh, Pakistan, Bhutan, Sri Lanka and Bali. Many overseas Indians in countries such as Burma, Singapore and Malaysia also adhere to Hinduism.
Buddhism has a great following in mainland Southeast Asia and East Asia. Buddhism is the religion of the majority of the populations of Cambodia (98%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020], Thailand (95%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020],Burma (89%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020],Japan (84-96%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020], Bhutan (75%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020],Sri Lanka (69%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020],Laos (67%-98%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020] and Mongolia (50%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020].Large Buddhist populations also exist in Singapore (42.5%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020],Taiwan (35.1%-93%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020] South Korea (23.2%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020],Malaysia(19.2%),Nepal(10.7%),[CIA Factbook,2010-2020] Vietnam (9.3-80%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020],China(8-80%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020],North Korea (4.5%-60%),Indonesia (<2%);and small communities in India and Bangladesh.
In many Chinese communities, Mahayana Buddhism is easily syncretized with Taoism, thus exact religious statistics is difficult to obtain and may be understated or overstated. The Communist-governed countries of China, Vietnam and North Korea are officially atheist, thus the number of Buddhists and other religious adherents may be under-reported.
Jainism is found mainly in India and in oversea Indian communities such as India and Malaysia. Sikhism is found in Northern India and amongst overseas Indian communities in other parts of Asia, especially Southeast Asia.
Confucianism is found predominantly in Mainland China, South Korea, Taiwan and in overseas Chinese populations.
Taoism is found mainly in Mainland China, Taiwan, Malaysia and Singapore. Taoism is easily syncretized with Mahayana Buddhism for many Chinese, thus exact religious statistics is difficult to obtain and may be understated or overstated.
Over 80% of the populations of both India and Nepal adhere to Hinduism, alongside significant communities in Bangladesh, Pakistan, Bhutan, Sri Lanka and Bali. Many overseas Indians in countries such as Burma, Singapore and Malaysia also adhere to Hinduism.
Buddhism has a great following in mainland Southeast Asia and East Asia. Buddhism is the religion of the majority of the populations of Cambodia (98%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020], Thailand (95%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020],Burma (89%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020],Japan (84-96%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020], Bhutan (75%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020],Sri Lanka (69%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020],Laos (67%-98%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020] and Mongolia (50%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020].Large Buddhist populations also exist in Singapore (42.5%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020],Taiwan (35.1%-93%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020] South Korea (23.2%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020],Malaysia(19.2%),Nepal(10.7%),[CIA Factbook,2010-2020] Vietnam (9.3-80%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020],China(8-80%)[CIA Factbook,2010-2020],North Korea (4.5%-60%),Indonesia (<2%);and small communities in India and Bangladesh.
In many Chinese communities, Mahayana Buddhism is easily syncretized with Taoism, thus exact religious statistics is difficult to obtain and may be understated or overstated. The Communist-governed countries of China, Vietnam and North Korea are officially atheist, thus the number of Buddhists and other religious adherents may be under-reported.
Jainism is found mainly in India and in oversea Indian communities such as India and Malaysia. Sikhism is found in Northern India and amongst overseas Indian communities in other parts of Asia, especially Southeast Asia.
Confucianism is found predominantly in Mainland China, South Korea, Taiwan and in overseas Chinese populations.
Taoism is found mainly in Mainland China, Taiwan, Malaysia and Singapore. Taoism is easily syncretized with Mahayana Buddhism for many Chinese, thus exact religious statistics is difficult to obtain and may be understated or overstated.
Economy Of Asia

Head Quarters of the People's Bank of China,Beijing, China-Centrl Bank of China
Asia has the third largest nominal GDP of all continents, after North America and Europe, but the largest when measured in PPP. As of 2010, the largest economies in Asia are China, Japan, India, South Korea and Indonesia.
Founded in 1893, Novosibirsk is the largest city in Siberia, with a population of about 1.5 million.
In the late 1990s and early 2000s, the economies of the PRC and India have been growing rapidly, both with an average annual growth rate of more than 8%. Other recent very high growth nations in Asia include Malaysia, Indonesia, Pakistan, Thailand, Vietnam, Mongolia, Uzbekistan, Cyprus and the Philippines, and mineral-rich nations such as Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Iran, Brunei, United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Bahrain and Oman.
February 2011 According to Citigroup 9 of 11 Global Growth Generators countries came from Asia driven by population and income growth. They are Bangladesh, China, India, Indonesia, Iraq, Mongolia, Philippines, Sri Lanka and Vietnam.
China was the largest and most advanced economy on earth for much of recorded history [2010], until the British Empire (excluding India) overtook it in the mid 19th century. Japan has had for only several decades after WW2 the largest economy in Asia and second-largest of any single nation in the world, after surpassing the Soviet Union (Measured in net material product) in 1986 and Germany in 1968. (NB: A number of supernational economies are larger, such as the European Union (EU), the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) or APEC).
In the late 1980s and early 1990s, Japan's GDP was almost as large (current exchange rate method) as that of the rest of Asia combined.In 1995, Japan's economy nearly equaled that of the USA as the largest economy in the world for a day, after the Japanese currency reached a record high of 79 yen/dollar. Economic growth in Asia since World War II to the 1990s had been concentrated in Japan as well as the four regions of South Korea, Taiwan, Hong Kong and Singapore located in the Pacific Rim, known as the Asian tigers, which have now all received developed country status, having the highest GDP per capita in Asia.
It is forecasted that India will overtake Japan in terms of nominal GDP by 2020 [Commonwealth Business Council-Asia 2007]. In terms of GDP per capita, both nominal and PPP-adjusted, South Korea will become the second wealthiest country in Asia by 2025, overtaking Germany, the United Kingdom and France. According to IMF statistics for the year 2010, the mostly unrecognised Republic of China PPP-adjusted GDP per capita, at USD 34,743, is already higher than that of Finland, France, or Japan. By 2027, according to Goldman Sachs, China will have the largest economy in the world.
Founded in 1893, Novosibirsk is the largest city in Siberia, with a population of about 1.5 million.
In the late 1990s and early 2000s, the economies of the PRC and India have been growing rapidly, both with an average annual growth rate of more than 8%. Other recent very high growth nations in Asia include Malaysia, Indonesia, Pakistan, Thailand, Vietnam, Mongolia, Uzbekistan, Cyprus and the Philippines, and mineral-rich nations such as Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Iran, Brunei, United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Bahrain and Oman.
February 2011 According to Citigroup 9 of 11 Global Growth Generators countries came from Asia driven by population and income growth. They are Bangladesh, China, India, Indonesia, Iraq, Mongolia, Philippines, Sri Lanka and Vietnam.
China was the largest and most advanced economy on earth for much of recorded history [2010], until the British Empire (excluding India) overtook it in the mid 19th century. Japan has had for only several decades after WW2 the largest economy in Asia and second-largest of any single nation in the world, after surpassing the Soviet Union (Measured in net material product) in 1986 and Germany in 1968. (NB: A number of supernational economies are larger, such as the European Union (EU), the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) or APEC).
In the late 1980s and early 1990s, Japan's GDP was almost as large (current exchange rate method) as that of the rest of Asia combined.In 1995, Japan's economy nearly equaled that of the USA as the largest economy in the world for a day, after the Japanese currency reached a record high of 79 yen/dollar. Economic growth in Asia since World War II to the 1990s had been concentrated in Japan as well as the four regions of South Korea, Taiwan, Hong Kong and Singapore located in the Pacific Rim, known as the Asian tigers, which have now all received developed country status, having the highest GDP per capita in Asia.
It is forecasted that India will overtake Japan in terms of nominal GDP by 2020 [Commonwealth Business Council-Asia 2007]. In terms of GDP per capita, both nominal and PPP-adjusted, South Korea will become the second wealthiest country in Asia by 2025, overtaking Germany, the United Kingdom and France. According to IMF statistics for the year 2010, the mostly unrecognised Republic of China PPP-adjusted GDP per capita, at USD 34,743, is already higher than that of Finland, France, or Japan. By 2027, according to Goldman Sachs, China will have the largest economy in the world.
Natural resources
Asia is the largest continent in the world by a considerable margin, and it is rich in natural resources, such as petroleum, forests, fish, water, rice, copper and silver.
Manufacturing in Asia
Manufacturing in Asia has traditionally been strongest in East and Southeast Asia, particularly in mainland China, Taiwan, South Korea, Japan, India, Philippines and Singapore. Japan and South Korea continue to dominate in the area of multinational corporations, but increasingly mainland China, and India are making significant inroads. Many companies from Europe, North America, South Korea and Japan have operations in Asia's developing countries to take advantage of its abundant supply of cheap labour and relatively developed infrastructure.